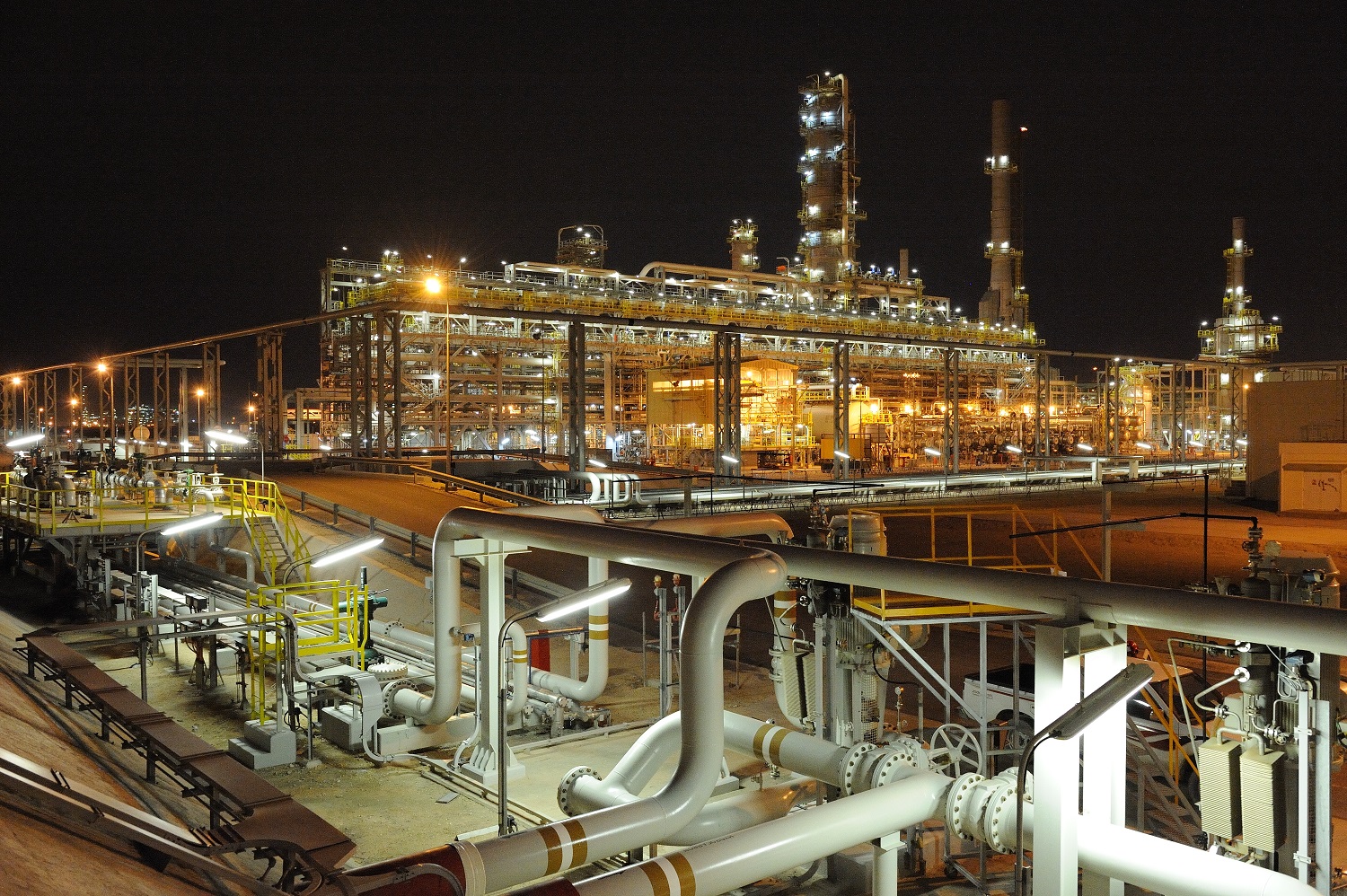
Kuwait’s plans to diversify its economy require increased oil revenues, but political deadlock is preventing crucial projects from moving ahead
For Kuwait, 2011 is a year of anniversaries. It will celebrate the 50th anniversary of the country’s independence, the 20th anniversary of its liberation from Iraqi occupation and the fifth anniversary of emir Sheikh Sabah al-Ahmad al-Jaber al-Sabah’s assumption of power.
Kuwait has a long-standing tradition of budgeting for a far lower oil price than forecast
For the economy, Kuwait has little to celebrate. The country is one of the most dependent on oil in the region, accounting for 45 per cent of its gross domestic product (GDP), 95 per cent of government revenue and 94 per cent of its exports. Plans for economic diversification are proving difficult to implement, with political wranglings frustrating its ambitions.
The headline economy is performing well. Local investment bank Kamco expects to see GDP growth of 7 per cent in 2011, based on forecasts of a 10 per cent recovery in non-oil GDP, the restoration of credit markets and a stabilisation in the real-estate sector, following the economic crisis. Oil GDP is expected to see modest growth of 4 per cent, although this could be increased if prices remain high during 2011.
Budget surplus in Kuwait
In the first nine months of 2010, the government’s total revenues were KD15.13bn ($55bn), more than double the original budget for the period, with the vast majority, KD14.12bn, coming from oil revenues. In May, the Central Bank of Kuwait reported that the provisional balance of payment figures for 2010 showed yet another rise in the country’s budget surplus, reaching KD10.5bn, compared with KD7.4bn in 2009.
Kuwait has a long-standing tradition of budgeting for a far lower oil price than forecast and this, in part, accounts for the surpluses it has run over the past decade. The remaining surplus, however, comes from another less positive tradition: below-budget spending.
The 2010 budget was based on an assumed oil price of $43 a barrel for the year, while the actual figure was far higher at $76 a barrel, leading to higher than budgeted revenues. But at the same time, expenditure was 34 per cent lower than projected.
| Kuwait GDP breakdown by sector, 2009 | |
|---|---|
| (Percentage) | |
| Oil and gas | 45 |
| Construction | 2 |
| Financial service | 14 |
| Manufacturing | 5 |
| Real estate | 4 |
| Transport and communication | 8 |
| Social and personal services | 18 |
| Wholesale and retail | 4 |
| GDP=Gross domestic product. Source: Global Investment House | |
The government launched a KD30bn development plan in February last year, its first since 1986, which called for increased spending on a wide array of megaprojects, the privatisation of public companies and a renewed focus on public-private partnerships (PPPs).
The Partnerships Technical Bureau (PTB) was established in 2009 with the aim of encouraging the private sector to participate in the development of projects in Kuwait. Its role is to conduct initial feasibility studies and surveys for identifying potential projects. The PTB plans to raise some $28bn by privatising and developing 32 projects on a PPP basis over the next five years. The schemes include developing low-cost housing, hospitals, universities, power plants and a series of transport projects. However, progress has disappointed with many projects slow to move forward.
Meanwhile, Kuwait’s attempts to rexpand its oil and gas industry over the past 15 years have been constantly frustrated by political deadlock. The National Assembly (parliament) is seen as the main sticking point for several stalled projects, including two long-delayed refining schemes. Officials point to intense political pressure when giving reasons for the cancellation of construction contracts for a new $15bn refinery project at Al-Zour in March 2009.
Economic diversification in Kuwait
The government hopes to use oil revenues to develop its non-oil economy. The Oil Ministry is aiming to raise production capacity to 3.5 million barrels a day (b/d) by 2015, from 3.1 million b/d currently, and to 4 million b/d by 2020. But this is looking difficult.
| Hydrocarbon reserves and production in Kuwait | |
|---|---|
| Oil production (thousand barrels a day) | 2,481 |
| Oil reserves* (billion barrels) | 101.5 |
| Oil proven reserves* (share of world total) | 7.6 |
| Gas production (billion cubic metres a day) | 12.5 |
| Gas proven reserves* (trillion cubic metres) | 1.78 |
| Gas proven reserves* (share of world total) | 1 |
| *At end of 2009. Source: BP Statistical Review of World Energy | |
The Washington-based IMF noted in August last year, that “unless progress is made towards oil sector project implementation, protracted capacity constraints could have a significant impact on revenues in the long term.”
On 8 May, Kuwait named a new oil minister, Mohammed al-Baseer, as part of its new cabinet to take over from Sheikh Ahmad Abdullah al-Ahmad al-Sabah, a member of Kuwait’s ruling family, who had led the ministry since February 2009. This follows the government’s resignation on 31 March, after members of parliament moved to question three ministers from the Al-Sabah family in parliament.
One of Al-Baseeri’s biggest challenges will be to kick-start Kuwait’s stalled refining projects, but despite the new appointment, oil analysts say little is likely to change in the near term.
The ongoing tug-of-war between the government and parliament, and the subsequent delays to the refining projects have been a big blow to the credibility of Kuwait on the international investment market.
Only recently, there was cautious optimism that Kuwait, while far from overcoming its bureaucratic deficiencies, was moving in the right direction. The ongoing deadlock in parliament will dampen the anniversary celebrations in Kuwait this year.
You might also like...

Rainmaking in the world economy
19 April 2024

Oman receives Madha industrial city tender prices
19 April 2024

Neom seeks to raise funds in $1.3bn sukuk sale
19 April 2024

Saudi firm advances Neutral Zone real estate plans
19 April 2024
A MEED Subscription...
Subscribe or upgrade your current MEED.com package to support your strategic planning with the MENA region’s best source of business information. Proceed to our online shop below to find out more about the features in each package.